Author: Habbisha Sivabalan
The world at present has a more significant population growth. India holds a population of 1.41 billion and is placed first in the ranking based on world population. The population growth is creating an immense increase in wants which is leading to greater levels of production and manufacturing of goods and services. The increase in labour availability also has influenced manufacturing levels and quantities and enabled India to emerge as a manufacturing hub.
The manufacturing sector has contributed approximately around 15% of the total GDP of India during the year 2022. According to IBEF, India holds the ability to become a global manufacturing hub by the year 2030 and can add more than US$ 500 billion annually to the global economy. The massive production has led to the need for sustainability.
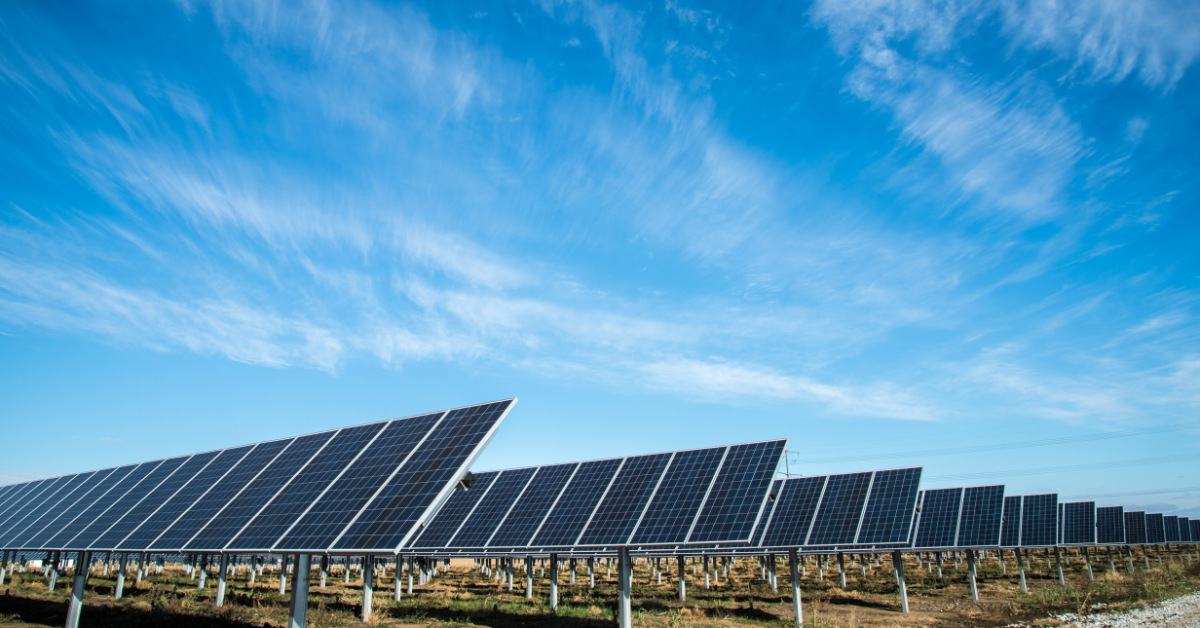
Sustainability in a broader sense is the ability of an economy to ensure that the present developments undertaken for production aid in maintaining and supporting the environment in the long run without compromising the needs of future generations. Sustainability focuses on production without creating an imbalance in the ecology. The economy, environment, and ecology are the three main pillars of sustainability. Also, sustainability is enhanced with the usage of renewable resources, and wastage generated is minimized leading to an increase in production efficiency.
Sustainability is a vital factor in the manufacturing sector. During the process of manufacturing, the entities need to ensure that natural resource depletion is prevented so that the resources will be available in the long run for future generations.
Sustainability in manufacturing has been taken into serious consideration by the government of India. India uses the formula of ‘TRIGGER’ for long-term sustainable growth in manufacturing. ‘TRIGGER’ is an acronym that stands for, Technology adoption, Reform in labour policy, Infrastructural reform, Good Governance, Education relevant for societal growth, and Resource (natural) management.
Some of the major initiatives undertaken and implemented by the government of India with the aim of sustainable manufacturing are namely,
- Zero Defect-zero Effect (ZED): The ZED initiative was implemented in the year 2016. ZED focuses on creating an ecosystem for competitive, qualitative, clean manufacturing, promoting the development of world-class products, and expanding the markets for MSMEs.
- Make-in-India: This Initiative was launched in the year 2014. Make-in-India aims to encourage MNCs and foreign companies to set up sustainable manufacturing plants in India.
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA): NMSA initiative was introduced in the year 2014-15. NMSA focuses on making agricultural production sustainable, remunerative, and climate resilient through promoting location-specific integrated farming systems and taking soil and moisture conservation measures.
- National Clean Energy Fund (NCEF): NCEF was set up in the year 2010-11. NCEF was founded to support the act deployment of renewable energy sourcing projects in the manufacturing sector.
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): NAPCC was introduced in the year 2008. The initiative was aimed at promoting a sustainable manufacturing process that would enable maintaining the climatic conditions.
These initiatives are focused on actively promoting sustainability in manufacturing while also creating momentum in economic growth. The major advantages that can be obtained by the Indian economy by following sustainable manufacturing methods such as Cost-effectiveness, Quality enhancement, Innovativeness to improve domestic consumption and Enhancing exports.
Technology is booming at present. Sustainability infused with technology could bring more benefits to the Indian economy as the country is emerging to become a manufacturing leader. Some of the main technological attributes that can be added to manufacturing activities to enable sustainability are
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): IIoT platforms aid in creating a connected manufacturing environment that enables the measurement of key Sustainability KPIs in real-time. It also helps manufacturers to reduce or eliminate their carbon footprint.
- Cloud: This element of technology would aid entities to accelerate the building of digital twins in the manufacturing process. This would minimize waste generation and enhance reuse.
- Blockchain: This would enable minimizing waste and capturing the sustainability metrics maintained by an entity from the beginning to the end of manufacturing activity.
In conclusion, India emerging as a manufacturing leader could implement sustainable product design and innovation, utilize renewable energy sourcing, infuse technological innovations for sustainable solutions, and engage in responsible waste disposal and waste management activities. These practices would collectively reduce the harm to the environment and enable India to become competitive in the global market space enabling the country to reap economic benefits.
References:
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/sustainability.asp
https://www.epa.gov/sustainability/sustainable-manufacturing
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0013935121015644